《Photoelectrocatalytic inactivation mechanism of E. coli DH5α(TET) and synergistic degradation of corresponding antibiotics in water》

DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118240
Website:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118240
Graphical Abstract:
ABSTRACT:
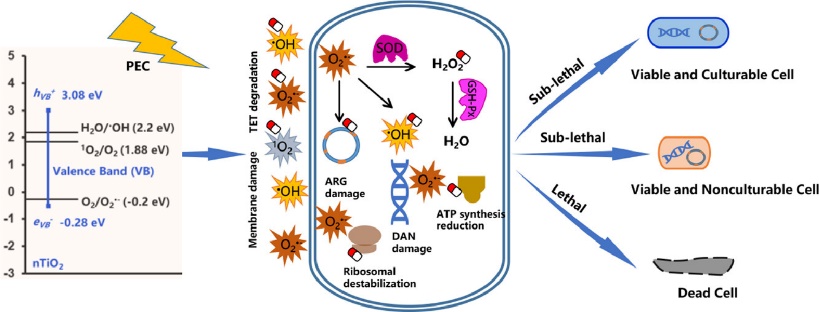
The occurrence and proliferation of antibiotic-resistance genes (ARGs) / antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) have been currently aggravating due to the increase of antibiotic residues in the aquatic environment. The interaction of ARB/ARGs with antibiotics inevitably occurred during water purification, yet their synergistic purification mechanism remains unclear. Herein, a systematic approach was developed to understand, in-depth, the synergistic mechanism in the coexisted E. coli DH5α (TET) inactivation and tetracycline hydrochloride (TET) degradation using photoelectrocatalysis (PEC) as a model technology. Results showed that low dosage (0 – 40 ppm) of TET exerted a negative influence on ARB inactivation with prolonged bactericidal time from 60 to 160 min. Addition of TET in environmental concentration (5 – 60 ppm) resulted in sub-lethal damage and prolonged PEC treatment time (100 – 160 min), accounting for inhibition effects on ARB inactivation. The major reactive species (RSs) involved in ARB inactivation and TET degradation were evidenced as photogenerated hole, •OH and O2•−, whereas hole and O2•−were demonstrated to be the major disinfectants for ARB/ARG inactivation. The bacterial defense system displayed increased antioxidative activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) to protect ARB cells against oxidative stress. Exposure to 60 ppm TET was a threshold where certain ARB cells were induced into viable but nonculturable bacterial cell (VBNC) state, as evidenced by plate counting and ATP activity analysis, together with the integral cell membranes observed by flow cytometry (FCM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). These findings appeal for appropriate technical adjustments for water and wastewater treatment to ensure safety of water.