
《Efficient Catalytic Combustion of Cyclohexane over PdAg/Fe2O3 Catalysts under Low-Temperature Conditions: Establishing the Degradation Mechanism using PTR-TOF-MS and in situ DRIFTS》
Website: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c14515
Graphical Abstract:
ABSTRACT:
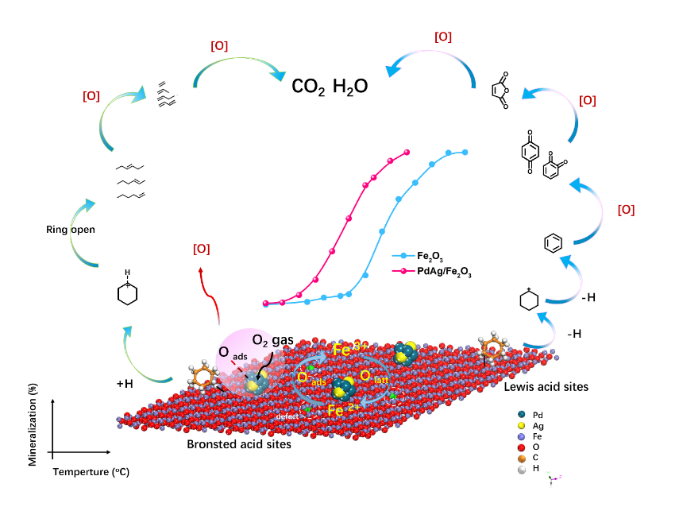
Cyclohexane, a typical volatile organic compound (VOC), poses high risks to the environment and humans. Herein, synthesized PdAg/Fe2O3 catalysts exhibited exceptional catalytic performance for cyclohexane combustion at lower temperatures (50% mineralization temperature (T50) of 199 oC, 90% mineralization temperature (T90) of 315 oC) than Pd/Fe2O3 (T50 of 262 oC, T90 of 335 oC) and Fe2O3 (T50 of 305 oC, T90 of 360 oC). In addition, PdAg/Fe2O3 displayed enhanced catalytic performance and stability, due to the low-temperature reducibility and the acidity of PdAg/Fe2O3 were enhanced by the PdAg alloy. In situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy and proton-transfer-reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry were applied to identify the intermediates formed on the catalyst surface and in the tail gas during oxidation, respectively. Results suggested that loading PdAg onto Fe2O3 significantly enhanced the adsorption and activation of oxygen and cyclohexane, oxidative dehydrogenation of cyclohexane to benzene, and catalytic cracking of cyclohexane to olefins at low temperatures. This in-depth study will benefit the design and application of efficient catalysts for the effective combustion of VOCs at low temperatures.