《Enhanced pizeopotential-mediated catalytic oxidation mechanism of formaldehyde and anti-deactivation performance onto ZnO surface》

Website:https://authors.elsevier.com/c/1ivoN3Id~t8x5~
Graphical Abstract:
Abstract:
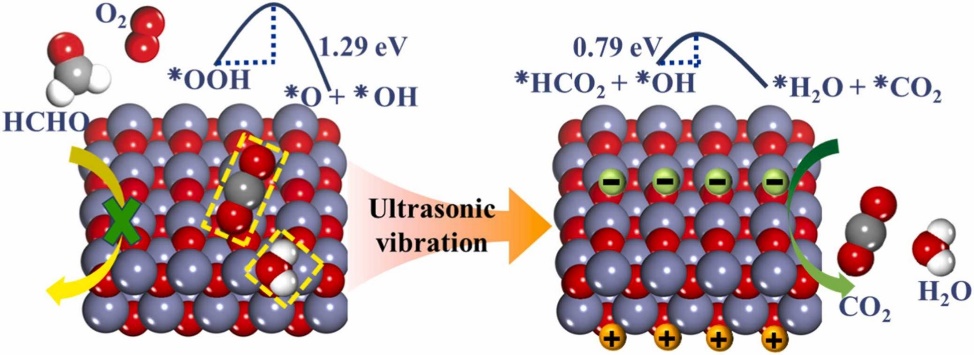
Effective formaldehyde catalytic oxidation at mild conditions to satisfy stringent environmental regulations is urgently required for conquering hazardous threats to ambient air and human health. The utilization of piezoelectric polarization induced by mechanical strain has emerged as a highly effective strategy for environmental remediation, tremendously promoting catalytic oxidation processes. Herein, first principles calculations integrated with piezoelectric model were utilized to explore formaldehyde oxidation on ZnO(100). The underlying quantitative relationship between adsorption capacity and external strain ratios was revealed, with a −12 % deformation ratio leading to optimal adsorption. Unexpectedly, the free energy barrier of rate determining step is significantly reduced in piezocatalytic system. Interestingly, ZnO under external compression not only exhibit effectively enhanced piezopotential activity, but also resolved the catalyst deactivation problem by removing CO2 and H2O from surface. This work highlights the role of piezopotential in VOCs catalytic oxidation, and suggests a strategy for designing piezoelectric catalysts.