《Research progress on secondary formation, photosensitive reaction mechanism and human health effects of chromophoric brown carbon》

Website:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2024.04.003
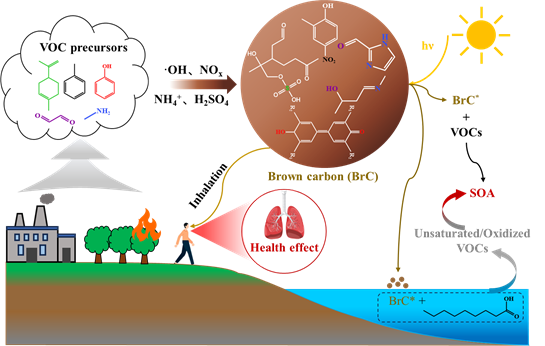
Graphical Abstract:
Abstract:
Brown carbon (BrC) has attracted widespread attention because of its strong absorption of solar radiation in the ultraviolet-visible wavelength range, which causes adverse impacts on human health. Originally, BrC was a physically defined class of substances. However, current research has gradually shifted towards the identification of its chemical groups, because its light-absorbing capability, chemical properties and health effects mainly depend on the chemical composition of its chromophores. Therefore, this review mainly focuses on the chemical understanding of BrC based on chromophores, and the secondary formation mechanism of chromophores, photosensitized reactions, and human health effects of BrC were detailly summarized. Firstly, BrC chromophores are divided into five categories: nitrogen-heterocycles, nitrogen-chain, aromatic species, oligomers and sulfur-containing organic compounds. Different chromophore precursor species exhibit variations, and their formation mechanisms are also distinct. Secondly, BrC can trigger the production of secondary organic aerosol (SOA) precursors or cause SOA growth because BrC is an important component of light-absorbing particles formed during incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels, potentially exerting adverse effects on human health. Finally, developing sufficiently separated methods for BrC and refining algorithms and machine learning can lead to a more effective understanding of the chemical composition of chromophores, thus enabling better evaluation of the atmospheric effects and health impacts of BrC. In all, this review provides new insights into the categories of BrC chromophores and new advance in secondary formation mechanisms, photosensitized reactions, and human health effects on the basis of chemical structures.