《Pyroelectric Pt-supported S-scheme heterojunction catalyst for effective photocatalytic degradation of VOCs containing soot driven by visible light》

Website: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2024.124858
Graphical Abstract:
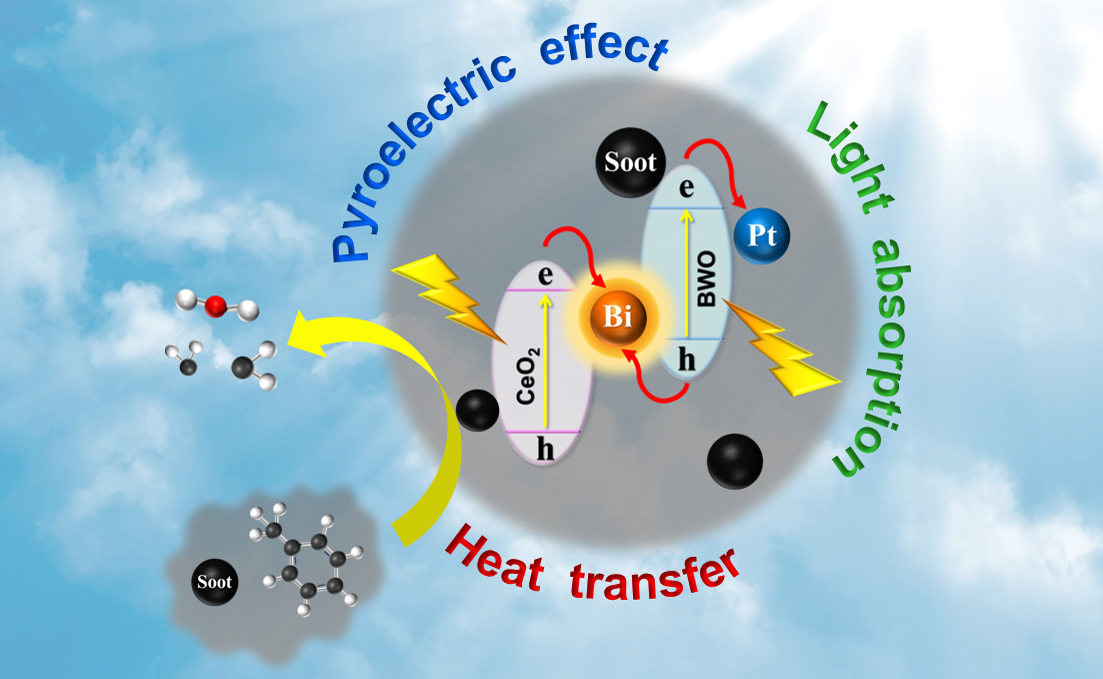
Abstract:
The trade-off between high visible-light response quantum yields and strong redox activity to achieve effective overall photocatalytic performance is still challengeable in the field of photocatalytic application. Herein, S-scheme heterojunction catalyst with high redox potential was developed by introducing small amount of Pt and excessive Bi into Bi2WO6 /CeO2(denoted as BWO/CeO2) through simple hydrothermal method, and applied to efficiently photocatalytic degradation of typical VOCs containing soot under visible light. It is experimentally proven that photogenerated charge transfer follows an S-scheme mechanism with interfacial Bi as a charge-transfer bridge and surface-deposited Pt as a photoexcited-electron trapper, which not only promotes charge separation but also enhances redox activity. Besides, both surface plasmon resonance of Bi nanoparticles and photothermal effect of soot trigger pyroelectric polarization of BWO to boost charge generation and separation, meanwhile induce photothermal synergistic effect of Pt/Bi-BWO/CeO2. All these beneficial factors lead to remarkably higher photocatalytic activity of Pt/Bi-BWO/CeO2 catalyst in comparison with single component of photocatalysts, with higher reaction rate constant of 2.3 times than BWO/CeO2 and 20.2 times than commercial CeO2. This work provides a visible photocatalytic strategy to efficiently purify VOCs containing soot, while perfectly transform soot pollutant into a valuable cocatalyst during catalytic processes.